The world of architecture is on the edge of a major shift, thanks to 3D printing technology. What started out as a novelty in small-scale manufacturing has grown into a powerful tool for building large structures. From eco-friendly homes to speedy construction of intricate designs, 3D printing is opening up new possibilities. This article dives into how 3D printing is becoming a growing trend in architecture and what it might mean for building in the future.
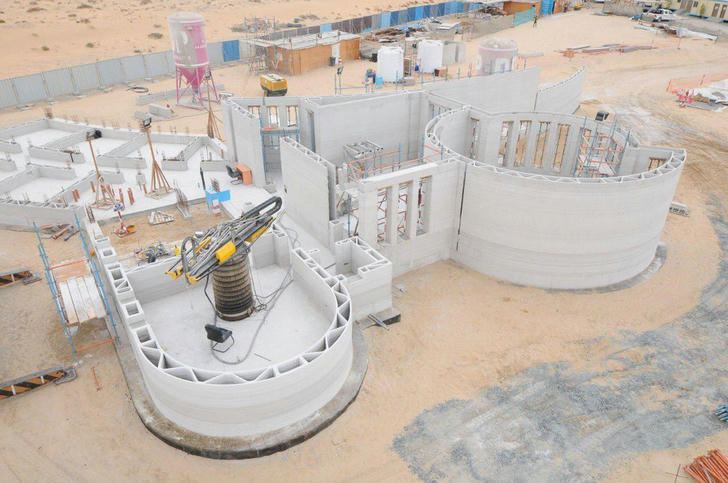

How 3D Printing Works in Building
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, creates objects layer by layer from a digital design. In architecture, materials like concrete, plastics, or composites are used to print whole buildings or parts of them. There are different types of 3D printers for construction, including gantry systems that move along fixed tracks, robotic arms, and mobile printers, all designed to handle large-scale projects.
Why 3D Printing Makes Sense for Construction
- Speed: One of the biggest perks is how fast it can be. Traditional builds can take months, but 3D printing can finish a house in just a few days. This is especially useful for quick emergency shelters or when large projects need to move fast.
- Lower Costs: It cuts down on manual labor and reduces material waste. Plus, printing on-site means less money spent transporting materials.
- Creative Freedom: Architects can design shapes and details that are tough or pricey to do with normal methods. Complex curves, organic forms, and intricate patterns become easier to create.
- Eco-Friendly: Sustainability matters more than ever. 3D printing helps by using less waste, cutting carbon emissions, and allowing recycled or local materials to be used.
Where 3D Printing Is Already Making a Difference
- Homes: Companies like ICON in Texas have built affordable houses quickly and cheaply using 3D printing, sparking interest worldwide in tackling housing shortages.
- Public Spaces: Bridges, parks, and pavilions have been printed in places like Madrid, showing how city infrastructure can benefit from this tech.
- Futuristic Designs: For those pushing design boundaries, 3D printing offers new ways to make customized, complex structures that traditional building methods struggle with.
- Disaster Relief: When time is critical, 3D printing can produce shelters and clinics fast, helping communities recover quicker.
Challenges Still on the Way

Even with all its promise, 3D printing in construction faces hurdles:
- Materials: Current printable materials mostly rely on concrete, which limits durability and variety. Developing stronger and greener materials is essential.
- Regulations: Building codes are made with traditional construction in mind, so new rules will be needed to ensure safety and standards for 3D-printed buildings.
- Scaling Up: Printing bigger, multi-story buildings is still tricky, especially in crowded cities where space and equipment logistics pose problems.
- Industry Adoption: Many builders are hesitant to jump in due to unfamiliarity and upfront costs. Getting everyone on board means cooperation between tech firms, architects, and regulators.
Looking Ahead: What the Future Holds
The potential of 3D printing in architecture is huge. One exciting idea is mass customization—where every building is tailored to the owner’s unique needs instead of cookie-cutter designs. This could change how homes and buildings are made forever.
As smart cities grow, 3D printing could be key in constructing energy-efficient, tech-integrated buildings that adapt to their environment. Plus, combining 3D printing with robotics might allow building in remote or extreme places—even on the Moon or Mars, as NASA explores.
In Conclusion
3D printing is quickly becoming a game-changer in how we build. It speeds up construction, cuts costs, and frees architects to dream bigger. While challenges remain, this technology is set to reshape everything from affordable housing and disaster relief to futuristic urban landscapes.
The future skyline will likely feature structures born from this blend of innovation and creativity. It’s not a question of if, but when 3D printing will become a dominant force in architecture, ushering in a bold new era for building worldwide.